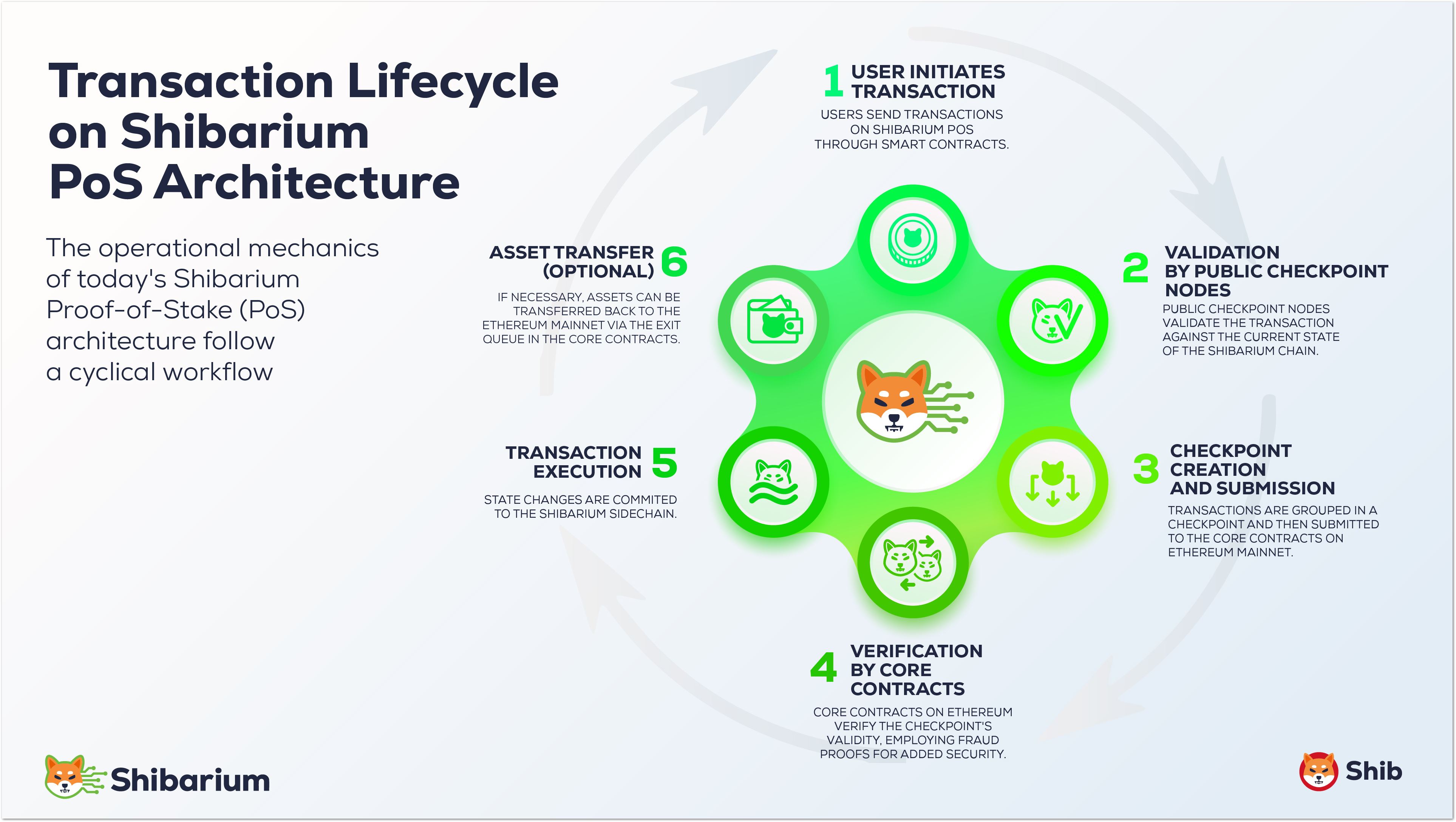
Shibarium PoS architecture is inspired by Polygon PoS, but uses BONE as the staking and governance token.
Architecture Layers
Ethereum (Main Chain)
Ethereum (Main Chain)
- Staking Contracts: Manage validator staking and delegation using BONE tokens.
- Checkpoint Contracts: Record periodic snapshots (checkpoints) of the Shibarium chain to Ethereum, ensuring data integrity and security.
- Rewards Contracts: Distribute staking rewards to validators and delegators.
Heimdall Layer
Heimdall Layer
- Proof of Stake: Heimdall is the validator layer responsible for managing validator sets, producing checkpoints, and relaying them to Ethereum. Validators stake BONE to participate in consensus and secure the network.
Bor Layer
Bor Layer
- EVM Compatibility: Bor is the block producer layer, fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), enabling seamless deployment of smart contracts and dApps.
- Fast Consensus: Bor achieves rapid block production and transaction finality, supporting high throughput and low fees.
How It Works
Stake BONE on Ethereum
Validators and delegators lock BONE tokens in staking contracts on Ethereum mainnet to participate in Shibarium’s PoS consensus.
Heimdall Validates and Checkpoints
Heimdall validators collect transactions, produce checkpoints, and submit them to Ethereum for security and finality.
Bor Produces Blocks
Bor nodes create blocks, execute EVM transactions, and maintain the Shibarium chain with fast consensus.
For more details, see the official Polygon PoS Architecture documentation (Shibarium is based on a similar design, but uses BONE and Shibarium branding).